Unleashing the Power of DAOs: The Benefits of Decentralized Autonomous Organizations in the Pacific
May 2023
Last year, the Marshall Islands in the Pacific became one of the first countries in the world to legalize DAOs an as organizational structure. This bold and visionary step has led to a dramatic increase in forward-thinking organizations turning to the Marshall Islands for where they establish their collaborative horizontal, decentralized, and holonomic organizations.
What Is a DAO?
If you’re wondering what this means and why is it a big deal, you are likely unfamiliar with the DAO concept or have only heard about it in passing.
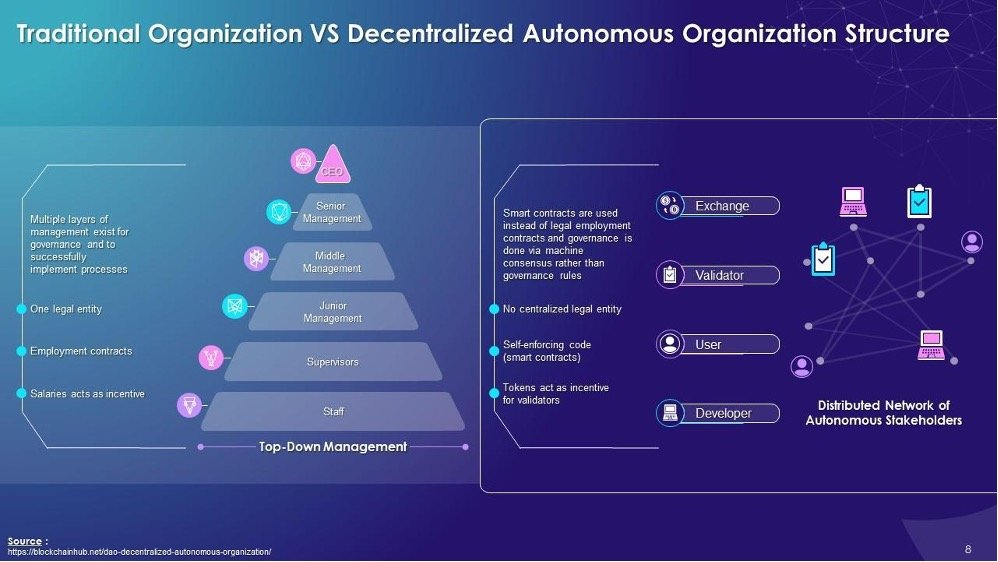
This acronym stands for Decentralized Autonomous Organization and refers to a bottom-up entity that has no central authority. This management structure also leverages blockchain technology to be fully transparent and autonomous.
A blockchain-governed organization collaborates and comes together because of a mutual mission where everyone who is a token holder of the DAO’s governance token is a stakeholder and participates as a member-owner of sorts. Governance votes utilize tokens created specifically for the DAO that are used to vote on proposals where consensus needs to be reached.
It is a novel concept that has some elements of other entity structures like co-ops, PMAs, starfish models, etc. Today, there are over 10,000 DAOs with market capitalization of nearly $10B in digital assets within their treasuries. These DAOs have over five million governance token holders, with around 1.5 million of them actively voting on governance proposals. We are a long ways away from the original Ethereum DAO in 2016 when only 11,000 people participated in this novel organizational structure.
Types of DAOs
Every decentralized autonomous organization has members who work together according to a specific set of shared rules that are programmed onto a blockchain like Ethereum. Ever since the first DAO in 2016, these flat-structure organizations have been increasingly impactful industry disrupters, be it in finance, humanitarian, or other sectors.
However, we need to emphasize that just because an organization calls itself a DAO does not mean it will be the same as another DAO. There are several different types of DAOs, with each kind serving a different purpose. Additionally, the benefits of DAOs will not be the same for each team or project.
Alchemy, 2022
Here are the main types of DAOs you should become familiar with:
● Protocol DAOs
● Philanthropy DAOs
● Social DAOs
● Collector DAOs
● Grant DAOs
● Investment & Venture DAOs
● Media DAOs
● Sub DAOs
Let’s briefly go over these main DAO types.
Protocol DAOs
A Protocol DAO uses on-chain tokens for voting purposes in order to implement changes to the protocol (a decentralized exchange, borrowing/lending dApp, etc.) or its finances.
Protocol DAO Examples:
● MakerDAO
● Uniswap
● Curve
● Yearn
Philanthropy DAOs
A Philanthropy DAO is focused on improving some aspect of society by organizing people around a unifying and shared purpose in order to create a meaningful impact.
Philanthropy DAO Examples:
● Big Green DAO
● Angel Protocol
● Endaoment
● Giveth
Social DAOs
A Social DAO is a decentralized and self-organizing community that has a platform connecting like-minded individuals for cross-pollination, collaboration, and coordination purposes.
Social DAO Examples:
● Seed Club
● Developer DAO
● Bright Moments DAO
● Cabin DAO
Collector DAOs
A Collector DAO is for supporting artists and NFT creators by pooling member funds so the DAO can invest its funds in valuable NFTs and digital collectibles representing physical assets like real estate.
Collector DAO Examples:
● FlamingoDAO
● ConstitutionDAO
● CityDAO
● RAW DAO
Grant DAOs
A Grant DAO is a community-funded DAO that provides grants to individuals and organizations looking to make a positive impact in the world.
Grant DAO Examples:
● Audius Grants
● MetaCartel
● Sevens Foundation
● Gitcoin DAO
Investment & Venture DAOs
An Investment and Venture DAO supports capital pooling from several decentralized finance (DeFi) investments and projects, and invests in early-stage Web3 startups where investment is not possible through traditional finance (TradFi).
Investment & Venture DAO Examples:
● BitDAO
● VC3 DAO
● BessemerDAO
● Venture DAO
Media DAOs
A Media DAO is a kind of decentralized community-driven news aggregator where DAO members actively earn profits. This kind of DAO prides itself in its transparency, focused on satisfying the common media interests of consumers.
Media DAO Examples:
● Mirror
● BanklessDAO
● Decrypt
● Take Up Space
SubDAOs
A SubDAO is a subset of DAO members who organize to manage specific functions, including operations, partnerships, marketing, grants, and more.
SubDAO Examples:
● Balancer
● Yield Guild Games
● DPG
● Helium
Benefits of DAOs in the Pacific
So, what are the benefits of decentralized autonomous organizations in the Pacific? Many of the benefits blockchain technology offers come preloaded into DAO architecture, including greater transparency, decentralization, efficiency, and more.
Increased Transparency
Here are some strategies DAOs use to improve transparency:
Open decision-making: In a DAO, every decision is reached through transparent voting that is open to all of the organization's members, not just C-suite executives or select stakeholders.
Records are accessible to the general public: All transactions and records are kept on a blockchain network that are viewable by the general public, which makes financial operations easily studied and referenced.
Immutable records: Once transactions get recorded on a blockchain, they cannot be changed. This provides a high level of openness and accountability by ensuring that all DAO transactions and decisions are forever recorded and can never be manipulated.
Elimination of middlemen: Since DAOs function on decentralized networks, no middlemen are engaged in decision-making. This enhances openness and removes the chance of any one entity or person being able to influence the organization's operations.
Enhanced Decentralization
DAOs excel when it comes to decentralizing governance and operations. Here is how:
Democratic and decentralized decision-making: A DAO is a self-governing entity that is capable of making choices on its own without the need for centralized authority. Thanks to this, decision-making is more democratic and decentralized because it involves a group of people, and not just a single individual or organization as a whole.
Leveraging smart contracts: DAOs are able to conduct trustless operations because they use smart contracts, which eliminates the need for needless middlemen. Because the laws of the organization are programmed into the DAO’s smart contract and automatically enforced, there is no longer any requirement for trust between parties.
Community governance: Communities of stakeholders who hold DAO tokens representing their ownership/involvement in the organization often manage DAOs. This means decisions can be made collaboratively rather than by a single authority.
Greater Efficiency
Every organization wants to be as efficient as possible. Here is how having a DAO leads to greater efficiency:
Automation: DAOs use smart contracts to automate decision-making and operations, which reduces the need for human intervention. This delivers faster, more efficient decision-making and execution of tasks.
Incentivization: DAOs create and use their own tokens to incentivize participation and reward contributors. This incentivization encourages DAO members to work harder and more efficiently, which delivers increased productivity and novel opportunities.
Flexibility: DAOs are designed to be highly adaptable and can evolve quickly to respond to changing circumstances. This flexibility allows DAOs to be more efficient in responding to new opportunities or challenges.
Increased Accessibility
A DAO also has the advantage of being highly accessible thanks to the internet. Here are the finer details of how it drives accessibility:
No geographically-limiting borders: There are no geographical restrictions because DAOs run on a global blockchain network. This allows for anyone to participate, as long as they simply have an internet connection.
Low barrier to entry: DAOs often have minimal entrance barriers since participation is usually based on digital token ownership rather than requiring a sizable financial investment or specific qualifications. This makes it possible for more people to join the organization, regardless of their financial situation or level of education.
Inclusive: DAOs are intended to be inclusive and democratic, with the community making decisions rather than a centralized authority. This makes room for a wider range of viewpoints and can guarantee that every DAO member has a voice in how the group operates.
Easier funding: DAOs are thriving in a number of sectors, including crowdfunding and project finance for decentralized organizations. A DAO contacts its stakeholders and other members to raise money by issuing native cryptocurrency tokens when a startup or project needs funding. The amount of tokens and voting credibility supplied to an investor depends on the investment margin.
Overall, keeping governance power and rewards decentralized allows everyone in an organization to have a say in the organization’s future, while also benefiting from the success the organization has. This makes DAOs enticing alternatives to traditional organizational structures.
Marshall Islands Trailblazing DAO Recognition
“With this adoption of the DAO Act of 2022, The Marshall Islands commits its courts and its resources to the burgeoning world of decentralization, and recognizes the unique place that decentralized autonomous organizations can hold not just in the blockchain space, but in the broader economy as well.”
Branson Wase, Finance Minister of the Republic of the Marshall Island
Any of the previously mentioned DAO types is now able to be a legal entity registered in the Marshall Islands if it adopts a DAO structure and governance tools. This small Pacific nation’s government is hoping this new law will encourage entities leveraging blockchain technology for their causes will call the Marshall Islands their home, as this will directly benefit the nation where the annual GDP is just slightly above $250M.
DAOs in the Marshall Islands will incorporate as limited liability companies (LLCs) but be officially classified as DAO LLCs. The nation makes it possible for both for-profit and nonprofit DAOs to become registered entities. What’s more is that the government had moved forward with creating an investment fund that will educate and train people about DAOs and integrate them more into their local economy.
The Marshall Islands sees that the world is going digital and that has led it to not only formally recognize DAOs but also explore various use-cases for digital assets like cryptocurrencies, NFTs, and more. In fact, the government is even looking into developing a blockchain-based cryptocurrency it is calling Sovereign (SOV).
Conclusion
As the blockchain and web3 ecosystems continue to grow and evolve, so too will the concept of DAOs and similar decentralized and distributed organizational structures. New models will appear, like DHOs (Decentralized Human Organizations) and others, which will continue to propel how we organize into groups for a shared purple into new realms of improved novelty.
We can thank the Marshall Islands for being one of the world’s governing trailblazers in this vein, and are likely to now see other nations in the Pacific and beyond begin adding DAOs to their legal frameworks so as many people can benefit as is possible.
Are you interested in learning more about how a DAO could benefit your organization, business, or cause? Contact us today and we would be happy to take the conversation further.
About the Author
Paul Lenda is a Digital Advisor at Pacific Advisory. He has a decade of experience working and operating within the blockchain industry, and advises on the responsible use of emerging & digital technologies, as well as adoption of regenerative systems, in a way that leverages benefits, reduces risks, and optimizes processes, resulting in improved socio-economic models.